with this latest news that Hussein Obama,, is going to allow the Russians,
full access to their nuclear weapons facilities, I am thinking people will
want to read this. I read it a couple of weeks ago, and think it's a good
time to post it.
We are supposed to be the most intelligent species on this tiny planet,,
we are also the only species capable of extincting this entire world,,
and EVERYTHING on it!
http://www.wired.com/politics/security/magazine/17-10/mf_deadhand?currentPage=all#

Listen: Author Nicholas Thompson Discusses Dead Hand on NPR's All Things Considered
Valery Yarynich glances nervously over his shoulder. Clad in a brown leather jacket, the 72-year-old former Soviet colonel is hunkered in the back of the dimly lit Iron Gate restaurant in Washington, DC. It's March 2009—the Berlin Wall came down two decades ago—but the lean and fit Yarynich is as jumpy as an informant dodging the KGB. He begins to whisper, quietly but firmly.
"The Perimeter system is very, very nice," he says. "We remove unique responsibility from high politicians and the military." He looks around again.
Yarynich is talking about Russia's doomsday machine. That's right, an actual doomsday device—a real, functioning version of the ultimate weapon, always presumed to exist only as a fantasy of apocalypse-obsessed science fiction writers and paranoid über-hawks. The thing that historian Lewis Mumford called "the central symbol of this scientifically organized nightmare of mass extermination." Turns out Yarynich, a 30-year veteran of the Soviet Strategic Rocket Forces and Soviet General Staff, helped build one.
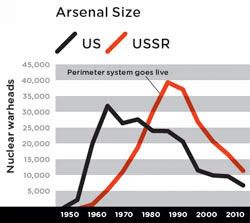 Chart source: Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists, Natural Resources Defense Council
Chart source: Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists, Natural Resources Defense CouncilThe point of the system, he explains, was to guarantee an automatic Soviet response to an American nuclear strike. Even if the US crippled the USSR with a surprise attack, the Soviets could still hit back. It wouldn't matter if the US blew up the Kremlin, took out the defense ministry, severed the communications network, and killed everyone with stars on their shoulders. Ground-based sensors would detect that a devastating blow had been struck and a counterattack would be launched.
The technical name was Perimeter, but some called it Mertvaya Ruka, or Dead Hand. It was built 25 years ago and remained a closely guarded secret. With the demise of the USSR, word of the system did leak out, but few people seemed to notice. In fact, though Yarynich and a former Minuteman launch officer named Bruce Blair have been writing about Perimeter since 1993 in numerous books and newspaper articles, its existence has not penetrated the public mind or the corridors of power. The Russians still won't discuss it, and Americans at the highest levels—including former top officials at the State Department and White House—say they've never heard of it. When I recently told former CIA director James Woolsey that the USSR had built a doomsday device, his eyes grew cold. "I hope to God the Soviets were more sensible than that." They weren't.
The system remains so shrouded that Yarynich worries his continued openness puts him in danger. He might have a point: One Soviet official who spoke with Americans about the system died in a mysterious fall down a staircase. But Yarynich takes the risk. He believes the world needs to know about Dead Hand. Because, after all, it is still in place.
The system that Yarynich helped build came online in 1985, after some of the most dangerous years of the Cold War. Throughout the '70s, the USSR had steadily narrowed the long US lead in nuclear firepower. At the same time, post-Vietnam, recession-era America seemed weak and confused. Then in strode Ronald Reagan, promising that the days of retreat were over. It was morning in America, he said, and twilight in the Soviet Union.
Part of the new president's hard-line approach was to make the Soviets believe that the US was unafraid of nuclear war. Many of his advisers had long advocated modeling and actively planning for nuclear combat. These were the progeny of Herman Kahn, author of On Thermonuclear War and Thinking About the Unthinkable. They believed that the side with the largest arsenal and an expressed readiness to use it would gain leverage during every crisis.

The new administration began expanding the US nuclear arsenal and priming the silos. And it backed up the bombs with bluster. In his 1981 Senate confirmation hearings, Eugene Rostow, incoming head of the Arms Control and Disarmament Agency, signaled that the US just might be crazy enough to use its weapons, declaring that Japan "not only survived but flourished after the nuclear attack" of 1945. Speaking of a possible US-Soviet exchange, he said, "Some estimates predict that there would be 10 million casualties on one side and 100 million on another. But that is not the whole of the population."
Meanwhile, in ways both small and large, US behavior toward the Soviets took on a harsher edge. Soviet ambassador Anatoly Dobrynin lost his reserved parking pass at the State Department. US troops swooped into tiny Grenada to defeat communism in Operation Urgent Fury. US naval exercises pushed ever closer to Soviet waters.
The strategy worked. Moscow soon believed the new US leadership really was ready to fight a nuclear war. But the Soviets also became convinced that the US was now willing to start a nuclear war. "The policy of the Reagan administration has to be seen as adventurous and serving the goal of world domination," Soviet marshal Nikolai Ogarkov told a gathering of the Warsaw Pact chiefs of staff in September 1982. "In 1941, too, there were many among us who warned against war and many who did not believe a war was coming," Ogarkov said, referring to the German invasion of his country. "Thus, the situation is not only very serious but also very dangerous."
A few months later, Reagan made one of the most provocative moves of the Cold War. He announced that the US was going to develop a shield of lasers and nuclear weapons in space to defend against Soviet warheads. He called it missile defense; critics mocked it as "Star Wars."
To Moscow it was the Death Star—and it confirmed that the US was planning an attack. It would be impossible for the system to stop thousands of incoming Soviet missiles at once, so missile defense made sense only as a way of mopping up after an initial US strike. The US would first fire its thousands of weapons at Soviet cities and missile silos. Some Soviet weapons would survive for a retaliatory launch, but Reagan's shield could block many of those. Thus, Star Wars would nullify the long-standing doctrine of mutually assured destruction, the principle that neither side would ever start a nuclear war since neither could survive a counterattack.
As we know now, Reagan was not planning a first strike. According to his private diaries and personal letters, he genuinely believed he was bringing about lasting peace. (He once told Gorbachev he might be a reincarnation of the human who invented the first shield.) The system, Reagan insisted, was purely defensive. But as the Soviets knew, if the Americans were mobilizing for attack, that's exactly what you'd expect them to say. And according to Cold War logic, if you think the other side is about to launch, you should do one of two things: Either launch first or convince the enemy that you can strike back even if you're dead.
Perimeter ensures the ability to strike back, but it's no hair-trigger device. It was designed to lie semi-dormant until switched on by a high official in a crisis. Then it would begin monitoring a network of seismic, radiation, and air pressure sensors for signs of nuclear explosions. Before launching any retaliatory strike, the system had to check off four if/then propositions: If it was turned on, then it would try to determine that a nuclear weapon had hit Soviet soil. If it seemed that one had, the system would check to see if any communication links to the war room of the Soviet General Staff remained.
If they did, and if some amount of time—likely ranging from 15 minutes to an hour—passed without further indications of attack, the machine would assume officials were still living who could order the counterattack and shut down. But if the line to the General Staff went dead, then Perimeter would infer that apocalypse had arrived. It would immediately transfer launch authority to whoever was manning the system at that moment deep inside a protected bunker—bypassing layers and layers of normal command authority. At that point, the ability to destroy the world would fall to whoever was on duty: maybe a high minister sent in during the crisis, maybe a 25-year-old junior officer fresh out of military academy.
And if that person decided to press the button ...
If/then. If/then. If/then. If/then.
Once initiated, the counterattack would be controlled by so-called command missiles. Hidden in hardened silos designed to withstand the massive blast and electromagnetic pulses of a nuclear explosion, these missiles would launch first and then radio down coded orders to whatever Soviet weapons had survived the first strike. At that point, the machines will have taken over the war. Soaring over the smoldering, radioactive ruins of the motherland, and with all ground communications destroyed, the command missiles would lead the destruction of the US.
The US did build versions of these technologies, deploying command missiles in what was called the Emergency Rocket Communications System. It also developed seismic and radiation sensors to monitor for nuclear tests or explosions the world over. But the US never combined it all into a system of zombie retaliation. It feared accidents and the one mistake that could end it all.
Instead, airborne American crews with the capacity and authority to launch retaliatory strikes were kept aloft throughout the Cold War. Their mission was similar to Perimeter's, but the system relied more on people and less on machines.
And in keeping with the principles of Cold War game theory, the US told the Soviets all about it.
Continue reading this Wired Article HERE






































No comments:
Post a Comment